Injection molding is a cornerstone process in manufacturing, widely used to produce high-precision plastic parts for a range of industries, from automotive and medical to consumer goods. While efficient and scalable, the process is not immune to defects. Detecting these flaws early is critical for ensuring product quality, reducing waste, and minimizing costly recalls. Today, manufacturers increasingly rely on Lincode AI solutions to enhance defect detection and streamline quality control in real time.
Below, we explore the most common defects found during injection molding inspections, their causes, and how advanced technologies like AI in manufacturing are helping solve these persistent challenges.
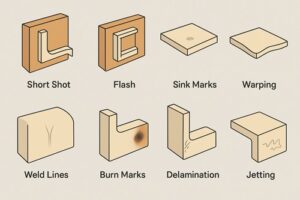
1. Short Shots
Short shots occur when the molten plastic fails to completely fill the mold cavity. This defect results in incomplete parts that are structurally weak and unusable.
Causes:
- Insufficient injection pressure
- Poor mold design
- Inadequate material temperature
Prevention: Manufacturers can address short shots by increasing the injection pressure or optimizing mold venting. Smart systems using machine learning can monitor flow patterns in real time and adjust parameters dynamically.
2. Flash
Flash, also known as burrs, appears when molten plastic seeps out of the mold cavity and solidifies along the parting line.
Causes:
- Excessive injection pressure
- Poor mold fit or damaged mold
- Incorrect clamping force
Prevention: Proper mold maintenance and calibration of machine settings are crucial. AI-based visual inspection tools are particularly effective in identifying even the smallest flash imperfections that human eyes might miss.
3. Sink Marks
Sink marks are small depressions or dimples that appear on the surface of molded parts, usually where material is thickest.
Causes:
- Improper cooling time
- Low packing pressure
- Inconsistent material flow
Prevention: Adjusting the cooling cycle and pressure levels can reduce sink marks. Tools powered by AI enable manufacturers to detect subtle surface defects immediately after ejection, allowing rapid corrective action.
4. Warping
Warping happens when different parts of a molded item cool and shrink unevenly, leading to twisting or bending of the part.
Causes:
- Uneven cooling
- Incompatible material composition
- Inadequate mold temperature control
Prevention: Maintaining uniform mold temperature and selecting the right material blend are key. Predictive analytics from systems like Lincode AI offer advanced defect prevention by forecasting where warping may occur and adjusting process parameters accordingly.
5. Weld Lines
Weld lines are visible lines or seams on the surface of molded parts where two flow fronts of molten plastic meet and solidify without properly bonding.
Causes:
- Low injection speed
- Inadequate mold temperature
- Poor gate placement
Prevention: Increasing mold and material temperature and optimizing flow dynamics can minimize weld lines. Automated inspection platforms can detect these lines faster than traditional methods, especially when integrated with computer vision.
6. Burn Marks
Burn marks are discolorations or dark spots on the part, typically near the edges, resulting from trapped air or excessive heat.
Causes:
- Trapped gases in the mold
- Excessive injection speed
- Degraded plastic material
Prevention: Ventilation enhancements and controlled injection speeds help prevent burns. AI systems equipped with thermal imaging can detect burn-related discoloration more accurately than manual checks.
7. Jetting
Jetting looks like squiggly lines on the surface of the part and happens when the plastic shoots into the mold too quickly without adhering smoothly.
Causes:
- High injection speed
- Poor gate design
- Inadequate material temperature
Prevention: Adjusting gate placement and reducing injection speed can help. Vision-based quality assurance platforms now provide automated feedback loops that detect and classify jetting defects within milliseconds.
8. Delamination
Delamination is the separation of material layers, causing a flaky or layered appearance. This defect compromises structural integrity and aesthetic value.
Causes:
- Contaminated material
- Incompatible resins
- Inconsistent heating
Prevention: Proper material selection and pre-processing can minimize delamination. With tools like Lincode AI, manufacturers can leverage pattern recognition to distinguish between delamination and other surface defects with high precision.
The Role of AI in Enhancing Quality Control
Traditional inspection methods—relying heavily on human labor—are not only time-consuming but also prone to inconsistency. With the integration of manufacturing with AI, companies are transforming their quality assurance systems.
AI-driven platforms collect and analyze data from vision systems, temperature sensors, and machine logs to detect, classify, and even predict defects. These technologies support adaptive control, meaning machines can modify their behavior in real time to correct deviations before a defect occurs.
Conclusion
Injection molding, though efficient, is susceptible to a variety of defects that can compromise product quality. Recognizing these common issues—short shots, flash, sink marks, and others—is the first step toward mitigation. By integrating modern tools like Lincode AI solutions, manufacturers can detect problems earlier, make smarter adjustments, and ensure consistent product excellence. As AI continues to evolve, the ability to deliver high-quality, defect-free parts will only become more precise and efficient.




Leave a Reply